BlackCat Ransomware That Breached Over 60 Organizations
The BlackCat ransomware that caused headaches for over 60 organizations worldwide is now decryptable, thanks to the effort of security researchers.
Yes, you read that correctly. The ransomware, first spotted in the wild in October 2019, can now be decrypted for free. It is a big deal because most ransomware cannot be decrypted, leaving organizations and individuals with no choice but to pay the ransom or lose their data forever.
Any guesses what is BlackCat ransomware? How it’s different from another ransomware? Read this blog and learn about this ransomware in detail.
What is BlackCat?
BlackCat ransomware is a file-encrypting malware that uses the AES-256 encryption algorithm to make users’ files inaccessible. It was first spotted in October 2019, and since then, it has been used in attacks against over 60 organizations worldwide. The attackers behind BlackCat ransomware are known for their efficient use of social engineering techniques.
For example- If one of their employees falls for a phishing email and opens an attachment, the BlackCat ransomware will automatically encrypt all of the organization’s data.
How is BlackCat it different from another ransomware?
Most ransomware uses the same encryption algorithm, which makes them decryptable. However, BlackCat uses the rust programming language, making it unique and more challenging to decrypt. It’s a new breed of ransomware.
The BlackCat ransomware is also different from other ransomware in its ability to spread laterally. Once it gains access to one system, it can apply to other systems on the same network quickly and easily. This makes it very difficult for organizations to contain the infection.
Let’s Understand How BlackCat Ransomware Works
When BlackCat ransomware first infects a system, it will check for any connected drives and network shares. If any are found, the ransomware will attempt to access them.
Once it has access, the BlackCat ransomware will encrypt all files on the drive or share. It will then display a ransom note that includes instructions on paying the ransom and decrypting the files.
The BlackCat ransomware is unique in that it uses the rust programming language, making it more difficult to decrypt than another ransomware.
Know Some Recent BlackCat Attacks
In February 2020, BlackCat ransomware was used in an attack against the City of Torrance, California. The attack resulted in the city’s email and phone systems being down for several days. It resulted in a loss of over $1 million. The city is still in the process of recovering from the attack.
In May 2020, BlackCat ransomware was used in an attack against the University of Michigan. The attack encrypted over 1,500 servers and 30,000 devices. Though the university has not yet released how much the attack cost them, it is believed to be in the millions of dollars.
BlackCat ransomware attacks have victimized at least 60 entities worldwide as of March 2022 since it was first spotted in November 2021.
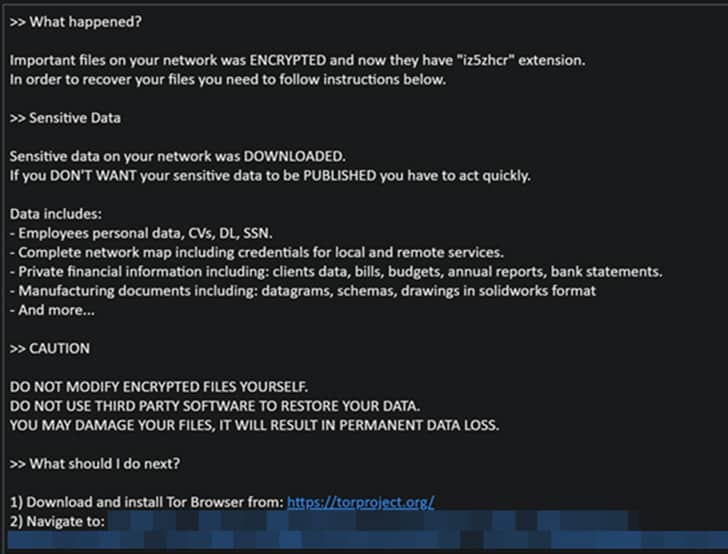
Austrian federal state Carinthia was also one of the victims of BlackCat ransomware. An employee opened a malicious email attachment, which led to the infection of over 300 servers. The attackers demanded a ransom of $5 million to unlock the encrypted computer systems.
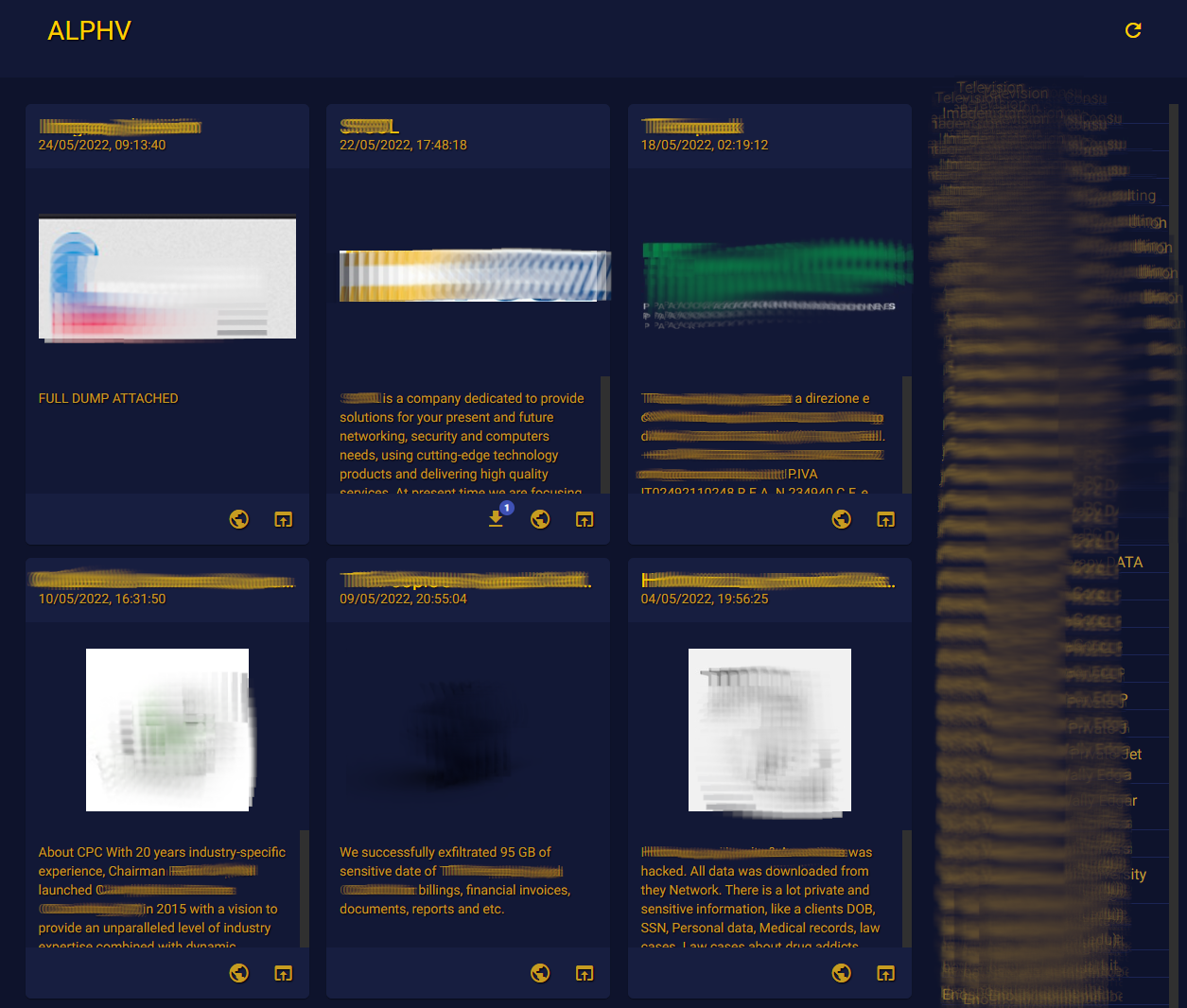
Latest victims announced in the ALPHV site
How to Protect from BlackCat Ransomware?
There are several steps that organizations can take to protect themselves from BlackCat ransomware.
- Educate employees about the dangers of phishing emails and attachments.
- Use strong spam filters to block phishing emails from reaching employees’ inboxes.
- Implement a data backup and recovery plan. It will ensure that your organization can recover from an attack even if the attackers demand a ransom.
- Use endpoint security solutions to block malicious attachments and prevent them from being executed.
- Use a firewall to block incoming connections from known malicious IP addresses.
- Keep your operating system and software up to date with the latest security patches.
- Implement least privilege principles, and it will ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and systems.
- Use an application whitelist to prevent unauthorized applications from being executed.
- Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to detect and block malicious activity.
- Regularly scan your network for vulnerabilities.
You can protect your organization from BlackCat ransomware and other threats by following these steps.
Conclusion
BlackCat is a new breed of ransomware that uses the rust programming language. It is more difficult to decrypt than another ransomware. BlackCat is also different from other ransomware in its ability to spread laterally. Once it gains access to one system, it can apply to other systems on the same network quickly and easily. This makes it very difficult for organizations to contain the infection.
Organizations can protect themselves from ransomware by taking steps to educate employees about phishing emails, implementing a data backup and recovery plan, and using endpoint security solutions. You can protect your organization from ransomware and other threats by following these steps.
So, what do you think of BlackCat ransomware? Do you think it’s a threat to organizations? Then Talk to Our Delivery Head
Relevant Blogs:
How do Cryptocurrencies Affect Cybersecurity?
MSSP’s Mitigation Responsibilities Against Ransomware
Spear Phishing: A Highly Targeted Phishing Attempt