Threat Modeling Unveiled: Enhancing Security in the Digital Age
In the fast-paced digital landscape, security breaches and data compromises have become prevalent. To counter these threats, organizations are turning to a powerful technique known as threat modeling. This blog explores the diverse use cases of threat modeling across industries, highlighting its significance for customers. We will delve into the technical aspects of it while captivating readers with insightful statistics and compelling narratives.
Types of Threat Modeling
It can take various forms, each providing a framework to address specific cybersecurity concerns. Two popular types of threat modeling are STRIDE and DREAD.
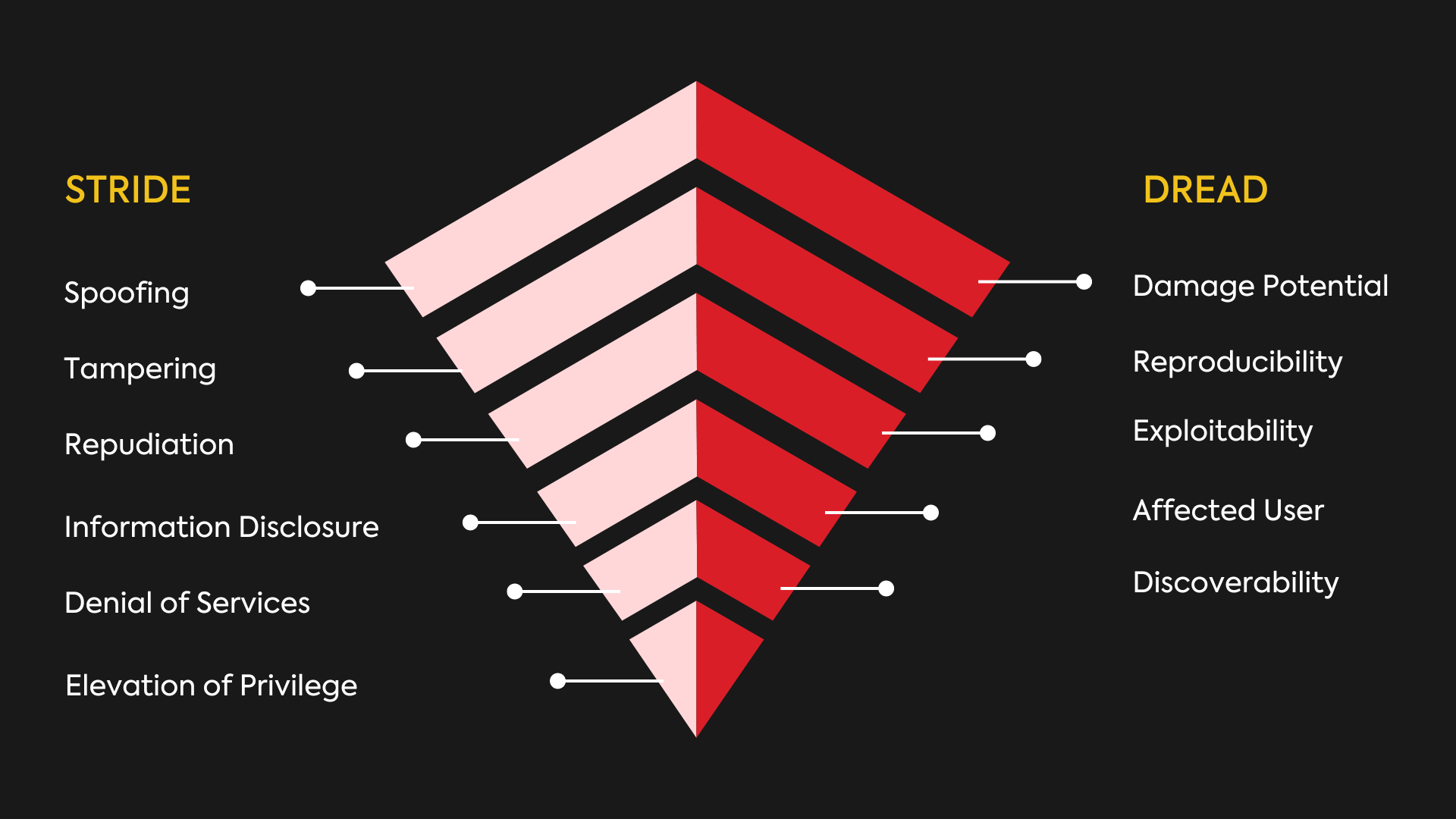
STRIDE: The STRIDE threat model, developed by Microsoft, focuses on six common cybersecurity threats:
- Spoofing: Unauthorized access to restricted networks or data by impersonating an authorized entity.
- Tampering: Malicious alteration of data or configuration files to gain unauthorized access or cause disruption.
- Repudiation: Denying responsibility for an attack without verifiable proof.
- Information Disclosure: Unauthorized leaks or breaches of sensitive or confidential data.
- Denial of Service: Overwhelming a system with superfluous requests, resulting in service disruption.
- Elevation of Privilege: Unauthorized access to files or data based on exploiting user privileges.
DREAD: DREAD helps organizations assess risks based on five key factors:
- Damage Potential: The potential impact a threat can have on the system or organization.
- Reproducibility: The ease with which a threat can be exploited repeatedly.
- Exploitability: The level of skill or effort required to exploit a vulnerability.
- Affected Users: The number of users or systems that can be impacted by a threat.
- Discoverability: The ease with which a threat can be discovered or identified.
Get Your Comprehensive Guide to Threat Modeling Today!
Use cases of Threat Modeling
Threat modeling is highly valuable in the early stages of the software development life cycle (SDLC) such as requirements gathering and design, where it helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in the system architecture.
Additionally, It is beneficial in infrastructure management, particularly in assessing and mitigating risks to critical assets such as networks, servers, and databases. By incorporating threat modeling at these key points, organizations can proactively address security concerns and implement appropriate security measures for robust protection.

- Proactive Risk Mitigation: By identifying and assessing potential threats in advance, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate risks and vulnerabilities.
- Optimal Resource Allocation: It helps businesses prioritize security investments and allocate resources effectively to address the most critical risks.
- Compliance with Standards: It assists in complying with industry standards and regulations by identifying potential risks to sensitive data and implementing necessary safeguards.
- Improved Collaboration: It encourages collaboration among different teams and stakeholders within an organization, ensuring a unified approach to cybersecurity.
Research indicates that 40% of companies that conducted root cause analysis (RCA) discovered that they could have avoided application security breaches if they had implemented threat modeling as part of their security strategy.
The Future
According to a recent study by a leading cybersecurity research firm, it was revealed that 33% of fintech and banking companies have adopted threat modeling as a proactive security measure by 2024. This significant adoption rate highlights the growing recognition of threat modeling as an effective approach to fortify security postures and prevent potential data breaches
Conclusion
Threat modeling is a powerful technique that allows organizations to proactively identify and mitigate security risks. By incorporating its technical components, businesses can enhance their security posture and protect valuable assets. The increasing industry adoption of threat modeling highlights its effectiveness in fortifying security strategies.