Get SAR Audit Report








The RBI Data Localization Mandate
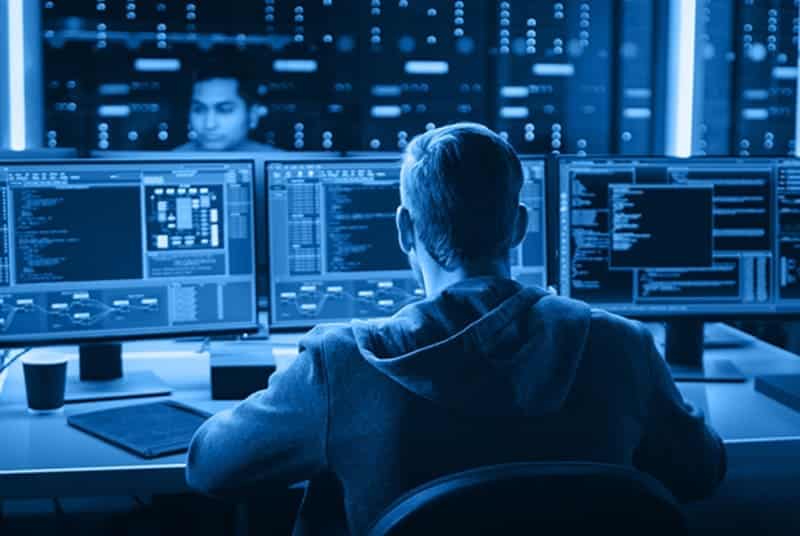
The Reserve Bank of India issued a directive vide circular DPSS.CO.OD.No 2785/06.08.005/2017-18 April 8, 2018, making it mandatory for all transaction data to be stored exclusively within India. As the central banking institution overseeing monetary policies, the RBI necessitates unrestricted supervisory access to payment data, leading to the enforcement of this mandate.
According to this mandate, all companies handling transactions in India, whether they’re global or local, like fintech companies doing peer-to-peer transactions or gateway operators handling global fund transfers, must keep all payment data within India.
What is SAR Audit?
The common vulnerabilities we tackled in the past
How does it work?
01
The audit, as outlined by the RBI, is to be conducted by auditors who are empaneled with CERT-IN (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team).
02
The SAR is expected to include a certification from the auditors confirming the completion of the data localization activity.
03
The SAR should be duly approved by the Board of the system provider, indicating that the organization's leadership is in agreement with and supports the findings and conclusions presented in the audit report.
04
Once the SAR is prepared, certified, and approved, it is then submitted to the Reserve Bank of India. This submission is a crucial step in demonstrating compliance with the regulatory requirement.
The Benefits of SAR Audits
Data Localization
Anti-Money Laundering
Enhanced IT Governance
How it works?
Audit Methodology
Audit Initiation
Document
Requirement List
Identification &
Analysis
Risk Response
Post-Deployment
Review
Do you know?
Want a quick Audit?
Key Data Requirements for System Audit Report for Data Localization (SAR)
Payment Data Elements
Classification of various data elements including payment credentials, transaction data, and customer information.
Transaction / Data Flow
Detailed diagram specifying the entire transaction flow, distinguishing between data at rest and in motion.
Application Architecture
Requirement for a comprehensive application architecture diagram detailing all involved components.
Online System Security
Assessment of controls ensuring security for payment information systems and mobile applications against malicious attacks.
Network Diagram / Architecture
Detailed network architecture diagram and adherence to a Network Security Policy.
Data Storage
Architecture diagram explaining data retention, along with a database architecture diagram and retention policy.
Transaction Processing
Detailed transaction/data flow with evidence of SOP or organizational policy.
Data Backup & Restoration
Compliance with guidelines for backup and restoration, supported by policies for Data Backup, Disaster Recovery, and Log Management.
Data Security
Verification of security controls such as masking, encryption, and policies for Data Security, Database Access Monitoring, and Data Purging.
Access Management
Assessment of data access from outside India and adherence to Access Control Checks in organizational policy.
Information Security Governance
Evaluation of top management's role in overseeing information security, supported by an Information Security Governance policy.
Asset Management
Requirements for hardware and change management, physical security, system scalability, and adherence to an Asset Management policy.
Human Resource Management
HR policy considerations for recruitment, training, and termination processes.
Business Continuity Management
Assessment of disaster recovery capabilities and BCP DR Plan.
Incident Management
Examination of the incident management policy and the organization's response mechanism to security incidents.
IT Project Management
Evaluation of controls for developing/acquiring new systems, focusing on project risk, and adherence to a Secure SDLC Policy.
Third-Party Risk Management
Assessment of controls for managing outsourcing risks, including vendor contracts, TPRM policy, and vendor outsourcing policy.
What do you get?
Audit Draft
Report
Remediation
Support
Final Audit
Report
Compliance
Letter
Detect & prevent attacks, before they succeed.
Stay ahead of the rapidly evolving threat landscape and keep your data protected without having to spend a fortune.