Devil for Modern Security: RANSOMWARE
Detail overview of trending issue in cyberspace, Ransomware

What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a kind of software or programming script which encrypts the user’s files and blocks the user from accessing their data. The new generation ransomware malware is built with advanced encryption algorithms(AES), which encrypts the data with the help of public and private key pair concepts. Once the machine gets infected with ransomware malware, it is almost impossible to decrypt the data without private keys, which are only owned by the attacker. Sometimes, the critical information gets infected with ransomware where the company needs to get the data back from the attacker at any cost. For the decryptor software and private keys, the attacker asks for ransom in cryptocurrency.
Types of Ransomware
There are mainly two types of a ransomware attacks.
- Online ransomware attack
- In this type of attack, an attacker firstly sends only the initial scripts which are very small in size and it is easy to bypass the antivirus and firewalls.
- Once the initiator enters the enterprise network, it downloads the different software like Cryptor, payloads, sometimes backdoor, etc.
- Once all the files are successfully downloaded, it starts infecting the server with the help of AES encryption keys. The private key will be shared to the attacker’s server, and then it starts encrypting files.
- In the worst-case, malware can also send sensitive documents to the attacker’s server. If an organization is denied to pay the ransom, an attacker can breach this sensitive information.
- This type of attack can be triggered with strong network monitoring and SOC.
- Offline ransomware attack
- In this type of attacker, an attacker needs to only drop a single malware, which can encrypt the files on its own.
- These types of attacks are very difficult to trigger as there will be no extra traffic and noise on the network. It works silently.
- In this type of attack, there is no chance of data breach as no data are being sent to the attack’s network.
How does it work?
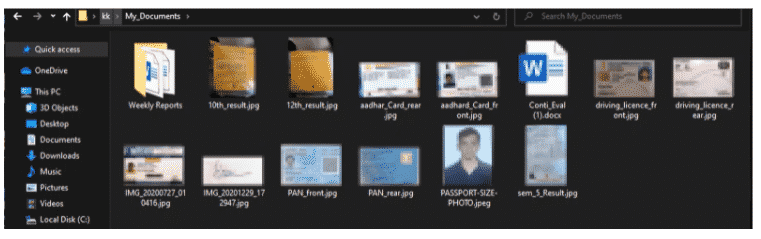
1. Pre-attack scenario: Before the ransomware attack, all files and folders are safe, which means a user can access the information easily.
2. Attack scenario: In the second phase the malware run in the background it encrypts the document in a very speedy manner. Before the user can understand what is going on, the malware successfully gets executed.
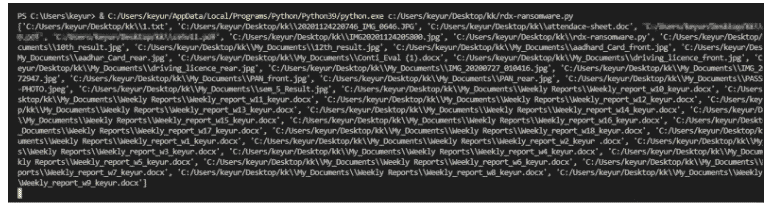
3. Post-attack scenario: After the successful attack, all the files are being encrypted with an advanced encryption method, if a user tries to access the file, as it is encrypted the information will be in nonreadable format.

Ransomware Demo
What are the challenges in a ransomware attack?
-
- Modern ransomware uses obfuscated methods to bypass detection systems.
- It uses the AES-1024 kind of encryption algorithm, which is next to impossible without keys.
- Data can be breached with the help of an online ransomware attack.
- Not only the particular machine, but modern ransomware can infect the whole network!
- These types of attacks are out of cyber insurance policy, which can make a bad impact on the financial position of an organization.
- It is hard to detect
- Most ransomware incidents are still unsolved today due to their complexity.
How to be secure from ransomware attacks?
In most cases, ransomware attacks happen due to the exploitation of publicly known security vulnerabilities and phishing campaigns.
- An attacker finds some security loopholes in the network or any assets of the organization and then tries to look for a vulnerable entry point. If they successfully find the vulnerable assets, they try to exploit the bug and install malware on the system. Which then starts infecting the data.
- In the second scenario the team of attacker target some particular mail server to land their malicious scripts inside the organization’s network. With the help of phishing mail, they send malicious attachments like (.exe), (.pdf), (.csv) etc. When an employee downloads the files the malware infection is initiated and starts infecting the systems.
To avoid this kind of information damage for a company, a company must take appropriate actions against ransomware attacks like below.
- Ensure to update the services and software to the latest version, so it will be difficult for an attacker to find the exploits and vulnerabilities.
- Ensure to backup sensitive data after fixed time intervals.
- Train the team for this kind of cyber-attack and spread awareness.
- Run a phishing campaign to get an idea about employee awareness.
- Use storage encryption to avoid data breaches.
Related Articles:
The 10 Biggest Ransomware Attacks of 2021- Infographic
Increasing Threat Of Ransomware to Online Business
How Not To Pay A Ransom: 3 Tips For Enterprise Security Pros

About Author
Keyur Talati
Security Analyst – WeSecureApp