Nonce: The Core Of Blockchain Security
Blockchain nonce! Have you ever heard the term? Do you want to learn what is nonce in blockchain? Find out in this article.
Blockchain has revolutionized the whole world. Be it healthcare, banks or any other sector has not remained untouched by its effect. From the latest survey, it’s found that there are over 83 million bitcoin block explorer blockchain.com wallets users worldwide as of July 2022. Where around 10% of the global population owns cryptocurrencies.
Now, around 16% of Americans have started investing in cryptocurrency. The decentralized ledger system of Blockchain helps the financial institution save up to $12 billion every year.
Indeed Blockchain has created great hype all around. But do you know there is a popular term called Nonce? It’s a popular term that was hidden under the shadows for years.
A nonce is a number or value you can use only once. In Blockchain’s context, it refers to a pseudo-random number utilized as a counter during mining. It is often used on authentication protocols and cryptographic hash functions.

For further understanding, continue reading this blog. We’ll uncover all the basics and its major significance in Blockchain. So, let’s get started.
What is Nonce?
A nonce is an abbreviation for ‘number used only once.’ In finance and cryptography, it is a randomly generated number used to verify transactions or perform security checks. It may seem simple, but it has a diverse range of use cases, including small transactions and space stations.
For instance, we often find captchas on websites that we must type to proceed. Even OTPs we receive via mail or phone to verify transactions are all nonces, having one-time use to verify something in a limited duration.
How Does Nonce Work in Blockchain?
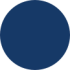
As discussed above, a nonce is a pseudo-random number used primarily as a counter in the mining process. For example, Bitcoin miners try and guess the correct nonce when they make multiple attempts to calculate a block hash complying with the specific requirements. Those who successfully find a nonce capable of a valid block hash get the right to add the following block to the blockchain. These miners also receive rewards for finding the nonce.
Mining is a comprehensive process involving many miners carrying out many hash functions with distinct nonce values. The primary objective is to get the correct output. When the miner’s hashing output exceeds the predefined threshold, the block is assumed valid and added to the blockchain.
If miners don’t get the correct output, they can try other nonce values until they get the right ones. Blockchain nonce’s search starts again after successful mining and the new block’s validation.
Significance in Blockchain
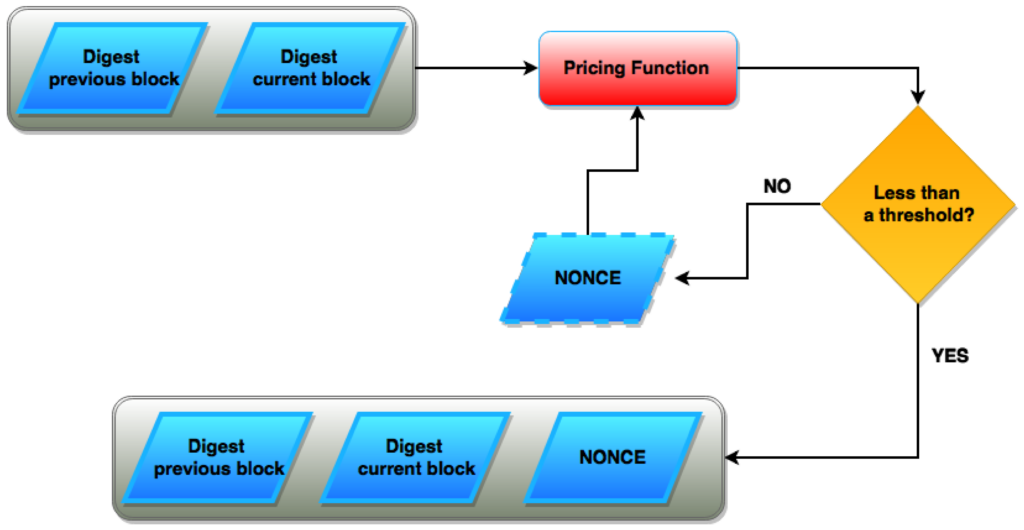
Nonce’s basics describe its significance well in Blockchain, as no transaction can be completed without it. In Bitcoin and other Proof of Work systems, the nonce seems mainly like a random number. Miners use the nonce for output testing of their hash calculations. Generally, miners use a trial-and-error method to estimate the nonce and utilize its new values in every calculation.
The nonce is a brute-force method to find the best rewards possibilities in a Proof-of-Work blockchain network. The main reason for guessing nonce values is the zero probabilities for guessing a correct nonce. Once you find the ‘golden nonce’ or the nonce that fits all the mining requirements of the next block, you can quickly move to the next block.
The rewards allocation for miners removes Bitcoins’ duplication possibilities or double-spending. It features consistent details, indicating the new block’s uniqueness. In addition, the field also changes in Proof of Work, irrespective of whether other areas change. Therefore, you can understand the nonce’s significance in blockchain for guiding miners toward the right route for rewards.
Struggle Behind Finding Nonce
When finding a nonce in Blockchain, you should know the whole process to avoid difficulties. The major difficulty everybody finds is the string you can use as the nonce. Guessing a random 32-bit string through a trial-and-error approach is quite tricky.
Miners have to guess the valid nonce and add it to the existing header hash, then rehash the value and compare it to the target hash. When the resulting hash value matches the requirements, miners can get the rewards for the block.
This guesswork in determining Blockchain nonce suggests miners must go through the million guesses before guessing the correct one. The difficulty of nonce estimation depends on the problem hash creation, which is lesser than the desired target.
The next difficulty of nonce guessing also affects the time needed for solutions. You can see that the block’s value difficulty remains the same throughout the whole blockchain network. Therefore, almost all miners get an equal opportunity to identify the correct hash.
In many cases, cryptocurrency blockchain networks set specific block targets they want to get verified at a particular time. When the blocks processed in a specific period do not meet the specified target, the network automatically lowers the difficulty level. Subsequently, cryptocurrency networks keep on adjusting the difficulty levels periodically to ensure compliance with desired targets.
Uses of Nonce
Nonce’s applications in the Proof of Work system are the best examples to show its significance in Blockchain. Here’s a list of the most notable uses of nonce values in Blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
- A promising tool in authentication protocols to safeguard old communications from reprocessing.
- Work as an initialization vector for data encryption use cases. You can use nonce values once to avoid repeated sequences in encrypted text.
- The most common use case of a nonce in the Blockchain is hashing in Proof of Work systems. The PoW systems generally leverage nonce values for changing the inputs in a cryptographic hash function. This results in miners complying with arbitrary mining requirements and achieving the desired difficulty.
- Some e-signature tools use blockchain nonce to create, compare, and verify signatures.
Concluding Thoughts
After reading this blog, it’s evident that nonce is at the heart of the PoW (Point of Work) consensus mechanism. Without the correct nonce, adding new blocks to the Blockchain is impossible. It is also a great way to secure the network and build users’ trust.