Don’t Leave Your Security to Chance: The Importance of Zero Security
In today’s ever-evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity is more important than ever. With hackers becoming more sophisticated and cybercrime increasingly commonplace, organizations must be proactive in protecting their data. One way to do that is through zero trust security, which emphasizes the need for robust authentication and access control measures.
Read on to learn about the foundations and principles of zero trust security, and how it can help ensure your data remains secure.
Introduction to Zero Trust Security
Zero trust security is a term for security models that don’t rely on predefined trust levels. In a zero-trust security model, all users and devices are treated in the same manner, whether inside or outside the network perimeter. This approach is in contrast to the traditional security model, which uses a “castle and moat” approach in which the goal is to keep bad actors out of the network by erecting a strong perimeter around it.
With zero trust security, there is no perimeter because access is based on need, not location. All traffic, both inbound and outbound, is treated with scrutiny. To do this, organizations need to have visibility into all activity on their network and must be able to verify the identity of users and devices.
Fundamentals of Zero Trust Security
Zero trust security is a term for security models that don’t rely on predefined trust levels. Devices and users are treated the same way, so cutting corners in the security process is impossible. Security is a fundamental element of using zero trust security—without it, the system wouldn’t work.
Zero trust security relies on verified identities to grant access to resources. These identities can be verified through something as simple as an email address or phone number, or they can be verified through more sophisticated means like two-factor authentication or biometrics. Once an identity is confirmed, users can access the resources they need.
There are three core principles of zero-trust security
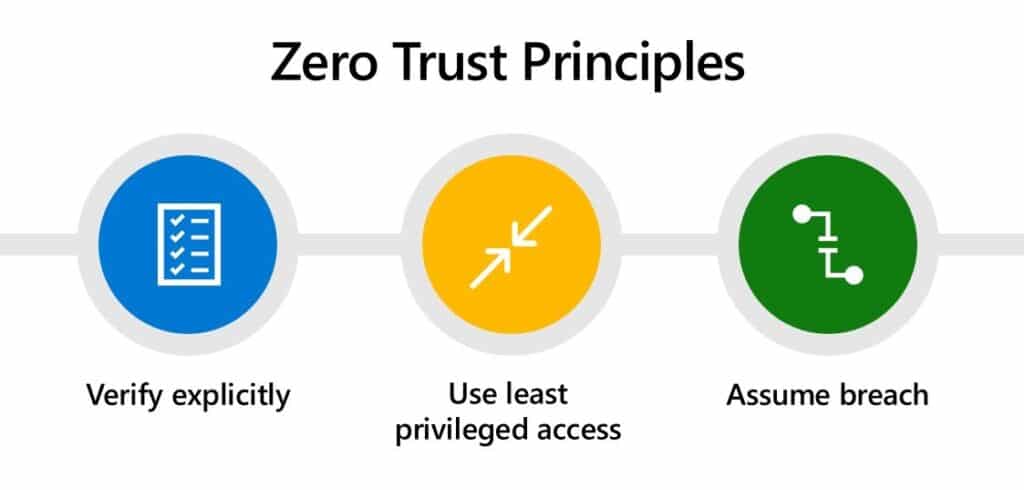
Source: Microsoft
- Verify explicitly – Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
- Least Privilege – The least privilege means that users are only given the permissions they need to do their job—no more and no less. It reduces your organization’s attack surface and helps contain the damage if an attacker does gain access to your systems.
- Assume breach – Minimize blast radius and segment access. Verify end-to-end encryption and use analytics to get visibility, drive threat detection, and improve defenses.
Benefits and Challenges of Zero Security
Security is a fundamental element of using zero trust security since all traffic is considered untrustworthy and must be verified before being allowed access.
The benefits of zero trust security include the following:
- Increased security: By its very nature, zero trust security eliminates many weak points that attackers can exploit.
- Improved efficiency: Zero trust systems are designed to be as streamlined as possible, so they can be more easily scaled and updated as needed.
- Greater transparency: Since all traffic is treated equally, it’s easier to see where potential problems may lie. This simplifies troubleshooting issues and identifying possible attacks before they cause damage.
However, zero security has its challenges. Some of the biggest challenges include the following:
- The learning curve: Implementing a zero-trust security system can be complex, so there’s a bit of a learning curve involved.
- Initial cost: Zero trust systems can be expensive to set up, especially if you need to replace legacy systems.
- Management overhead: Zero trust systems require ongoing management and monitoring to be effective, which can add to the overall cost.
Implementing a Zero Security Solution
Zero trust security is a term for security models that don’t rely on predefined trust levels. In other words, with a zero-trust security solution, no user, device, or service is automatically trusted. Everyone must be verified and authenticated before being granted access to data or systems.
There are many benefits to implementing a zero-trust security solution, including increased security and improved efficiency. By not automatically trusting anyone or anything, you eliminate the potential for weak points in your security posture. And because authentication and authorization checks are done on a per-request basis rather than in advance, users can easily access the resources they need to do their job.
If you’re considering implementing a zero-trust security solution, there are a few things you need to keep in mind:
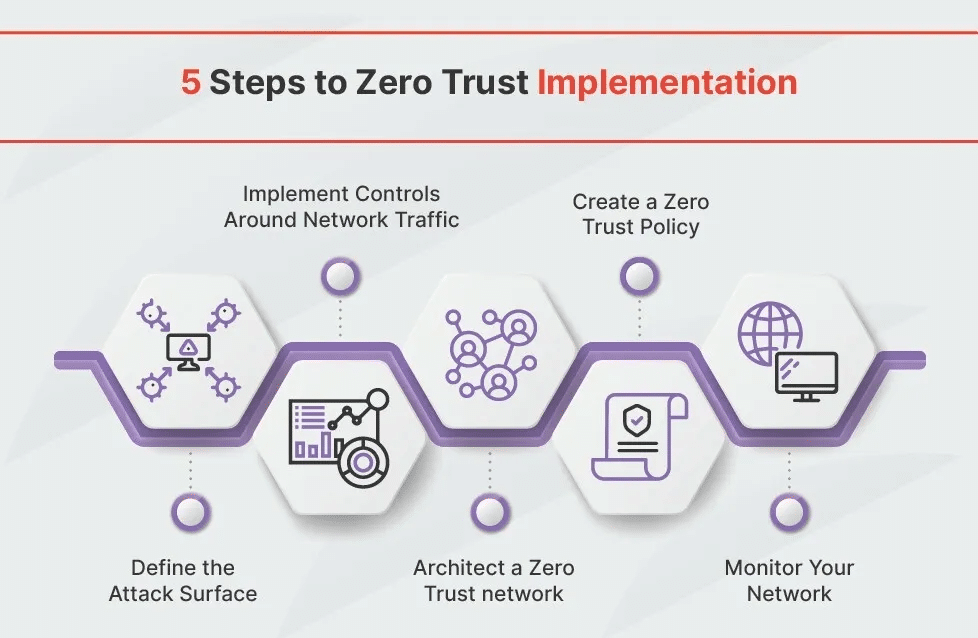
- You need to clearly understand what assets need to be protected and who should have access to them.
- You need to have the right tools in place to verify identities and enforce access controls.
- You must ensure all your employees know the new security procedures and know how to follow them.
Use Cases for Zero Security
Zero security is a term for security models that don’t rely on predefined trust levels. In a zero security model, all users and devices are treated as untrusted until they’ve been verified.
There are a few different use cases for zero security:
- When sensitive data is being accessed: Zero security can be used to protect sensitive data from being accessed by unauthorized users. By verifying the identity of users and devices before allowing them to access data, you can be sure that only authorized users will be able to see it.
- When multiple devices need to be authenticated: If you have multiple devices that need to be authenticated (e.g., a laptop and a smartphone), zero security can be used to verify each device’s identity before allowing access. This way, you can be sure that only authorized devices can access your data.
- When there’s a possibility of an attack: Zero security can also be used as a defense against attacks. By constantly verifying the identities of users and devices, you can make it more difficult for attackers to gain access to your systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, deploying a Zero Trust Security system is essential in today’s digital world. Its layered approach to security allows organizations to protect their data and resources from malicious threats.
Furthermore, its robust authentication process helps ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information. As more companies move towards cloud-based systems and increase their reliance on digital tools, zero security will become increasingly crucial for protecting businesses against cyberattacks.