The Major Types of Phishing Attacks & How to Identify Them: The Definitive Guide
Every data breach begins with a phishing attack. To prevent your organization from becoming the next victim, you need to understand the different types of phishing attacks and how to identify them.
Phishing is a type of cyberattack that uses fraudulent emails or websites to trick victims into sharing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial information.
According to a survey, 91% of cyberattacks begin with phishing emails. There are different phishing attacks, and each uses another method to trick victims.
This blog will discuss the common types of phishing attacks and how to identify them. So, read on to learn more.
Types Of Phishing Attacks & Tips To Identify Them
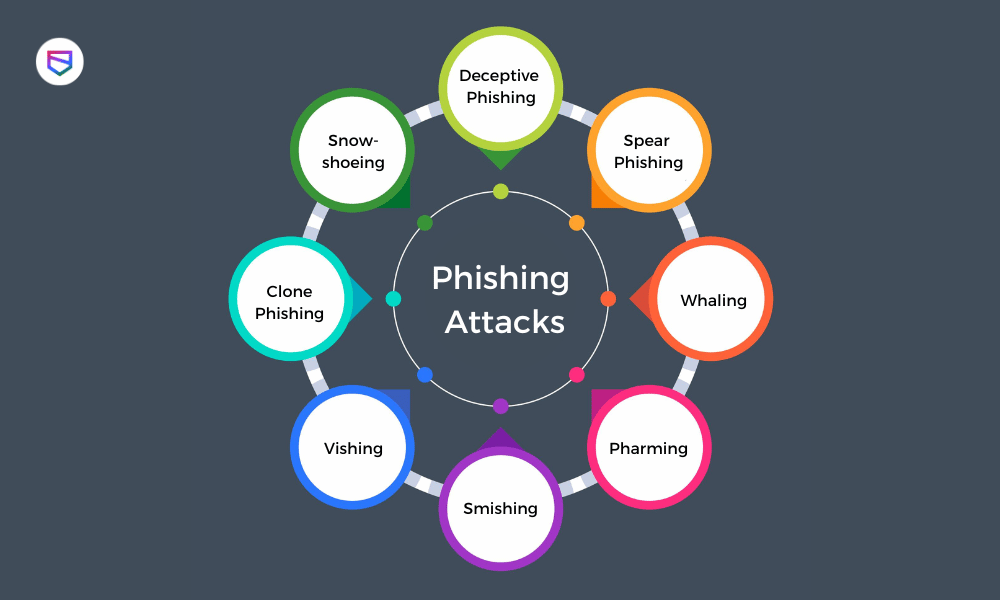
1) Deceptive Phishing: Mass-market E-mails
Deceptive phishing is the most common type of phishing attack. It uses fraudulent emails or websites that look like they’re from a legitimate source, such as a company or organization.
The attacker will usually spoof the email address or website to make it look real. They may also use logos or other graphics from legitimate sources to make the email or website look more convincing.
Deceptive phishing attacks often steal login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data. They can also be used to install malware on a victim’s computer or device. Test your organization’s coordination capabilities when an incident takes place
For example- In 2017, a deceptive phishing attack targeted Netflix user. The attackers sent emails that looked like they were from Netflix, asking the recipients to update their payment information.
The email had Netflix’s logo and branding, and it directed users to a fake website that looked like the actual Netflix website.
If users entered their payment information on the fake website, the attackers would steal their credit card numbers and other sensitive data.
How to identify deceptive phishing attacks?
Deceptive phishing attacks can be challenging to identify because they look like legitimate emails or websites. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- If you’re not expecting an email from the sender, be suspicious.
- If the email has poor grammar or spelling mistakes, it may be a phishing email.
- If the email or website looks different from the usual format, it may be a phishing attack.
These are just a few of the red flags to look out for. If you’re ever unsure about an email or website, don’t click on any links or enter any information.
Instead, contact the company or organization directly to verify the email or website.
2) Spear Phishing: Personalized Emails
Spear phishing is a phishing attack that uses personalized emails to target specific individuals or organizations.
The attacker will usually have information about their targets, such as their name, job title, or company. They’ll use this information to make the email look more convincing.
For example- In 2016, a spear-phishing attack targeted employees of the Democratic National Committee (DNC). The attackers sent emails that looked like they were from Google, asking the recipients to update their Google account information.
The email had the Google logo and branding, directing users to a fake website that looked like the actual Google website. If users entered their login credentials on the fake website, the attackers would steal their account information.
How to identify spear-phishing attacks?
Spear phishing attacks can be challenging to identify because they often look like legitimate emails. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- If you’re not expecting an email from the sender, be suspicious.
- If the email has poor grammar or spelling mistakes, it may be a phishing email.
- If the email is addressed to you by name, it may be a spear-phishing attack.
All of these are red flags that should make you suspicious of an email. If you’re ever unsure about an email, don’t click on any links or enter any information. Instead, contact the company or organization directly to verify the email.
3) Whaling: Emails Targeting High-Profile Individuals
Whaling is a phishing attack that uses emails to target high-profile individuals, such as CEOs, CFOs, and other executives.
The attackers will usually have information about their targets, such as their name or position at the company. They’ll use this information to make the email look more convincing.
For example- In 2020, a whaling attack targeted the employees of a major U.S. company. The attackers sent emails that looked like they were from the company’s CEO, asking the recipients to transfer money to a new bank account.
The email had the CEO’s name and branding, directing users to a fake website that looked like an actual company website. If users entered their login credentials on the fake website, the attackers would steal their account information.
How to identify whaling attacks?
Whaling attacks can be challenging to identify because they often look like legitimate emails. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- Any email that asks you to transfer money or make payment should be treated with suspicion.
- If the email is addressed to you by name, it may be a whaling attack.
- If the email is from a high-profile individual, such as a CEO or CFO, it may be a whaling attack.
- Attackers will often try to rush you into taking action, so be suspicious of any email that asks you to act immediately.
These are common indicators of a whaling attack. If you’re ever unsure about an email, don’t click on any links or enter any information. Better yet, don’t even open the email. Instead, contact the company or organization directly to verify the email.
4) Pharming: Redirecting Traffic to Fake Websites
Pharming is a phishing attack that uses fake websites to trick users into entering their personal information.
The attackers usually send out spam emails containing links to fake websites. Users who click these links will be redirected to the phony website without realizing it.
The fake website will look identical to the actual website and have the same branding and logo. However, the URL will be slightly different. For example, a phishing website for Facebook might have a URL that looks like this:
www.faceb00k.com.
When users enter their login credentials on the fake website, the attackers will steal their account information.
How to identify pharming attacks?
Pharming attacks can be challenging to identify because fake websites look identical to real ones. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- Check the URL of the website before you enter any information. If the URL is different from the actual website, it may be a phishing website.
- It may be a pharming attack if you’re being redirected to a website without clicking on a link.
- Attackers will often try to rush you into taking action, so be suspicious of any website that asks you to act immediately.
These are common indicators of a pharming attack. If you’re unsure about a website, don’t enter any information. For better security, you can install an anti-phishing toolbar that will warn you if you’re on a phishing website.
5) Smishing: Phishing Attacks via SMS
Smishing is a phishing attack that uses text messages (SMS) to trick users into giving away their personal information.
The attackers will send out text messages that appear to be from a legitimate company or organization. The text message will usually contain a link to a fake website.
Users who click on the link will be redirected to the fake website without realizing it. The fake website will look identical to the actual website and have the same branding and logo.
However, the URL will be slightly different. For example, a phishing website for Amazon might have a URL that looks like this:
www.amazon.com.co.uk
When users enter their login credentials on the fake website, the attackers will steal their account information.
How to identify smishing attacks?
Smishing attacks can be challenging to identify because text messages look identical to legitimate companies’ messages. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- Be suspicious if you’re being asked to click on a link in a text message. Legitimate companies will rarely ask you to do this.
- If the text message is from a high-profile individual, such as a CEO or CFO, it may be a smishing attack.
- Attackers will often try to rush you into taking action, so be suspicious of any text message that asks you to act immediately.
These are common indicators of a smishing attack. If you’re unsure about a text message, don’t click on any links or enter any information. There’s no harm in contacting the company directly to verify the message.
6) Vishing: Phishing Attacks via Voice Calls
Vishing is a phishing attack that uses voice calls (typically made over VoIP) to trick users into giving away their personal information.
The attackers will impersonate a legitimate company or organization and call the victim. They will then try to trick the victim into giving away personal information, such as a credit card or social security number.
How to identify vishing attacks?
Vishing attacks can be challenging to identify because the attacker will sound like a legitimate representative from a company or organization. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- If you’re being asked to give away personal information, be suspicious. Legitimate companies will never ask for this type of information over the phone.
- If you’re being asked to act immediately, it may be a vishing attack. Attackers will often try to rush you into taking action.
These are common indicators of a vishing attack. Try to verify the caller’s identity by asking for their name, department, and contact information. If you’re still unsure, hang up and call the company directly to verify the message.
7) Clone Phishing: Attacks that Use Cloned Emails
Clone phishing is a type of phishing attack that uses a clone of a legitimate email to trick users into giving away their personal information.
The attacker will start by stealing a legitimate email from the victim’s inbox. They will then create a clone of the email and change the URL in the message to a link to a fake website.
There are two types of clone phishing attacks:
1) attackers can create a replica of the original email and send it to the victim
2) attackers can create a replica of the original email and send it to the victim’s contacts
How to identify clone phishing attacks?
Clone phishing attacks can be challenging to identify because they use a legitimate email that has been cloned. However, there are some red flags that you can look for:
- If you receive an email replica of an email you’ve received before, it may be a clone phishing attack.
- Be suspicious if you’re being asked to click on a link in an email. Legitimate companies will rarely ask you to do this.
- If the email is from a high-profile individual, such as a CEO or CFO, it may be a clone phishing attack.
These are common indicators of a clone phishing attack. If you’re ever unsure about an email, don’t click on any links or enter any information. There’s no harm in contacting the company directly to verify the message.
8) Snowshoeing: Spamming from Multiple IP Addresses
Snowshoeing is spamming that uses multiple IP addresses to send large volumes of email. It gets its name from the analogy of a snowshoe, a type of shoe that helps you distribute weight over a large area.
This type of spamming is difficult to detect because it uses multiple IP addresses, making it appear that the emails are coming from multiple sources.
How to identify snowshoeing attacks?
There are some indicators that you can look for to identify a snowshoeing attack:
- It may be a snowshoeing attack if you’re receiving a large volume of emails from the same sender.
- If the emails come from multiple IP addresses, it may be a snowshoeing attack.
- If the emails come from multiple addresses, it may be a snowshoeing attack.
These are common indicators of a snowshoeing attack. If you think you’re snowshoeing, contact the company or organization supposedly sending the emails to verify the message.
Conclusion
So, these are some of the most common types of phishing attacks. Be sure to keep an eye out for these attacks, and never give away your personal information to someone you don’t know. If you think you’re being attacked, contact the company or organization supposedly sending the emails to verify the message. Cybersecurity awareness is an ongoing process of educating and training employees about the threats that lurk in cyberspace.
Related Articles:
How to Mitigate Phishing Attacks in Your Organization?
How contact forms can be exploited to conduct large scale phishing activity?
Browser-in-the Browser (BITB) – A New Born Phishing Methodology