Pentesting in the Healthcare Industry: An Approach to Enhance Healthcare Cybersecurity
The healthcare sector has experienced remarkable technological advancement and transformation, lately. As technology continues to shape the healthcare industry so does the risk/cyber threat landscape. With healthcare organizations relying on digital platforms and electronic health records (EHRs) that store sensitive patient information, payment data, and medical Internet of Things devices it becomes an attractive target for cyber attackers.
According to AtlasVPN, In 2023, data breaches impacted 87 million patients in the United States, marking a more than twofold increase from the 37 million affected in 2022.
The growing incidence of cyber assaults on healthcare organizations emphasizes the significance of cybersecurity measures. To protect information and ensure the security of healthcare systems pentesting has become a crucial element of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
Cybersecurity challenges in the healthcare sector
In recent years the growing value of data on illegal markets has led to a significant surge in cyber assaults against the healthcare sector. Ransomware attacks, data breaches, and other forms of cyber threats are becoming more prevalent posing a threat to patient privacy and disrupting healthcare operations. The emergence of electronic health records (EHRs) and interconnected medical devices has expanded the attack surface granting malicious actors additional opportunities for unauthorized access.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) serves as the framework in this domain mandating that all companies handling protected health information adhere to specific procedures. However, even for well-prepared organizations maintaining HIPAA compliance has become a demanding task despite the established legal framework.
Healthcare organizations face the challenge of aligning their security protocols with the evolving threat environment while strictly adhering to HIPAA’s stringent regulations.
Potential Consequences:
- HIPAA Compliance or HITECH Penalties
- Breach Lawsuit/Legal Fees
- Operational Downtime
- Loss of Patient trust or data
- Financial Losses
- Brand Damage
- Loss of Business Opportunities
Understanding the importance of pentesting
Pentesting, also known as Penetration Testing, is a proactive approach to mimic the tactics used by malicious hackers. It is a systematic strategy for detecting and correcting vulnerabilities in a system, network, or application.
The importance of penetration testing cannot be emphasized in the healthcare sector, where the repercussions of a security compromise can be disastrous. Pentesting, by simulating the mindset of a potential attacker, assists firms in staying one step ahead of cyber adversaries.
1. Identifying vulnerabilities before exploitation
Pentesting enables healthcare businesses to proactively uncover and resolve vulnerabilities before malicious actors attack them. This approach allows for the identification of patterns and root causes, enabling the prevention of future network vulnerabilities. Key features like remediation time, CVSS scores on detected vulnerabilities, vulnerability categorization, and vulnerability locations throughout the network can be identified.
2. Compliance with regulatory standards
In healthcare, ensuring compliance with severe standards such as HIPAA is critical. Pentesting has evolved into a proactive tool, allowing enterprises to strengthen their security posture in accordance with these requirements. Through thorough tests, vulnerabilities are identified and addressed, mitigating the risk of data breaches, avoiding legal repercussions, and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive healthcare information.
3. Securing connected medical devices
As linked medical devices proliferate, new entry points for cyber threats emerge. Penetration testing broadens its scope to include evaluation of these devices to ensure they are resistant to cyber threats and do not jeopardize patient safety.
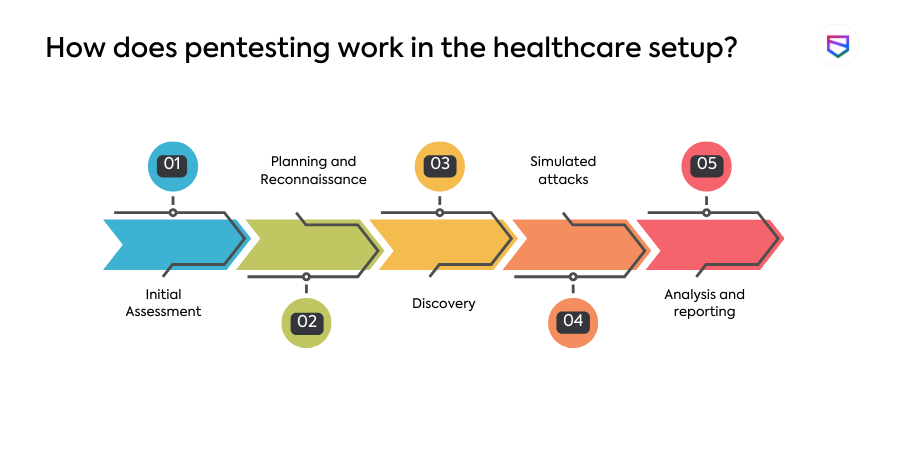 1. Initial Assessment
1. Initial Assessment
The pentesting process begins with a comprehensive assessment of the healthcare organization’s digital ecosystem, identifying potential entry points for cyber threats. The test’s aim and goals are established, and the scope of the pentesting is defined. Legal considerations are also taken into account.
2. Planning and Reconnaissance
Ethical hackers plan and conduct reconnaissance to obtain information about the organization’s infrastructure, including vulnerabilities and potential attack routes. This involves mapping out the target’s network or application and understanding its functionalities.
3. Discovery
This step is divided into two parts: more information collection and vulnerability scanning. To obtain extra information, techniques such as DNS interrogation, banner capturing, and internal system enumeration are utilized. Vulnerability scanning may be done either manually or automatically.
4. Simulated attacks
To find weaknesses that may be exploited by malicious actors, ethical hackers/pen testers mimic a range of cyber attacks, including phishing attempts, network incursions, and application exploits. Post exploitation, the pentester assesses the value of the entry point, ease of maintaining access, potential breach detection time, and potential harm caused.
5. Analysis and reporting
The pentesting test results are extensively reviewed, and a complete report is delivered to the healthcare company. A Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) report contains detailed information on vulnerabilities, such as descriptions, ratings, severity, impact, risk assessment, and video proof-of-concepts (POCs). Recommendations for addressing vulnerabilities and strengthening cybersecurity measures are also offered.
These steps comprise a complete approach to penetration testing, assisting healthcare companies in identifying and correcting any security flaws in their systems and applications.
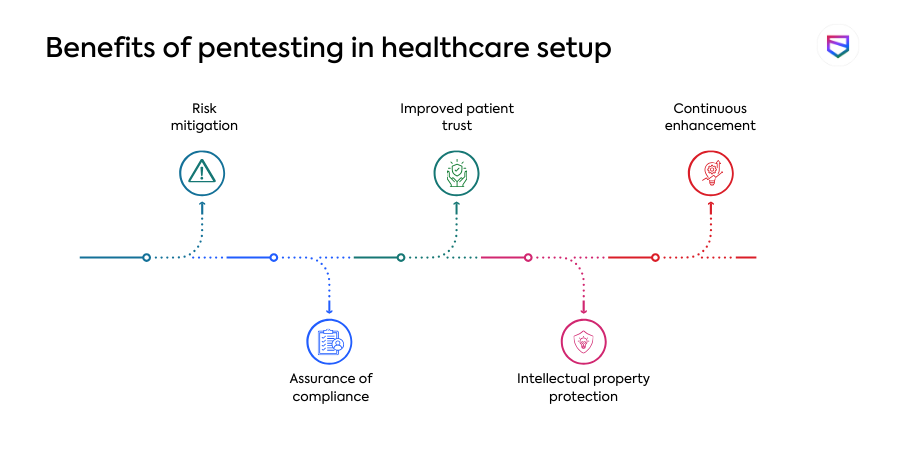
Penetration testing is a key protection mechanism in the face of rising cyber threats in the healthcare sector.
1. Risk mitigation
Addressing vulnerabilities proactively minimizes the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational harm.
2. Assurance of compliance
Pentesting assists healthcare firms in demonstrating regulatory compliance and avoiding legal and financial fines.
3. Improved patient trust
Healthcare providers increase patient trust by investing in cybersecurity measures, ensuring individuals that their sensitive information is protected.
4. Intellectual property protection
Penetration testing protects intellectual property and research data from illegal access and theft.
5. Continuous enhancement
Penetration testing on a regular basis enables healthcare firms to keep ahead of new cyber threats, adjust security solutions, and maintain a solid cybersecurity posture.
The WeSecureApp approach
WeSecureApp recognizes the crucial relevance of cybersecurity in the healthcare industry. Our penetration testing/pentesting services are targeted to healthcare businesses’ specific needs and concerns, providing a full audit of their digital infrastructure. We utilize a team of expert ethical hackers that replicate real-world attack scenarios in order to find and remediate vulnerabilities, eventually strengthening our clients’ cybersecurity posture.
WesecureApp’s services include:
- Web application pentest
- Mobile application pentest
- Cloud/Network pentest
- Endpoint security
- Red teaming
- Social engineering testing
FAQs
- How frequently should healthcare businesses do penetration tests?
Answer: Penetration testing should preferably be done at least once a year. The frequency, however, may vary depending on factors like the size of the business, the complexity of its digital infrastructure, and changes in the threat landscape. Regular testing assists in proactively identifying and addressing problems.
- What factors should healthcare companies consider when choosing a penetration testing provider?
Answer: Healthcare organizations should consider the provider’s experience in the healthcare sector, the expertise of their ethical hacking team, compliance with industry regulations, the comprehensiveness of their testing services, and the effectiveness of their reporting capabilities when selecting a penetration testing provider. A successful cybersecurity plan requires selecting a vendor who understands the special demands of the healthcare business.
- Is penetration testing required for healthcare businesses as part of regulatory compliance such as HIPAA?
Answer: While not technically required, penetration testing is widely recommended for healthcare businesses, particularly those subject to rules like HIPAA. Regular testing assists in discovering and correcting security flaws, complying with compliance requirements, and demonstrating a commitment to patient data protection.
- What role does penetration testing play in securing connected medical devices in healthcare?
Answer: Penetration testing broadens its reach to assess the security of medical equipment that is linked together. Ethical hackers examine the resilience of these devices by simulating various cyber-attacks, ensuring they are resistant to threats.